Tet, above all, is an opportunity for the household genies to meet, those who have helped during the year, namely the Craft Creator, the Land Genie and the Kitchen God. Learn more here.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1
The "Mam Ngu Qua"
2
Dao, Mai, Quat (the Peach, Apricot and Kumquat)
3
The giao thua (New Year's eve)
4
Food specialties for TET
Tet - Vietnamese Lunar New Year is the most important festival of Vietnamese people. This sacred festival sometimes falls between late January or early February (depends on Lunar Calendar) and Tet has become so familiar to the Vietnamese that when Spring arrives, the Vietnamese, wherever they may be, are all thrilled and excited with the advent of Tet, and they feel an immense nostalgia, wishing to come back to their homeland for a family reunion and a taste of the particular flavors of the Vietnamese festivities.
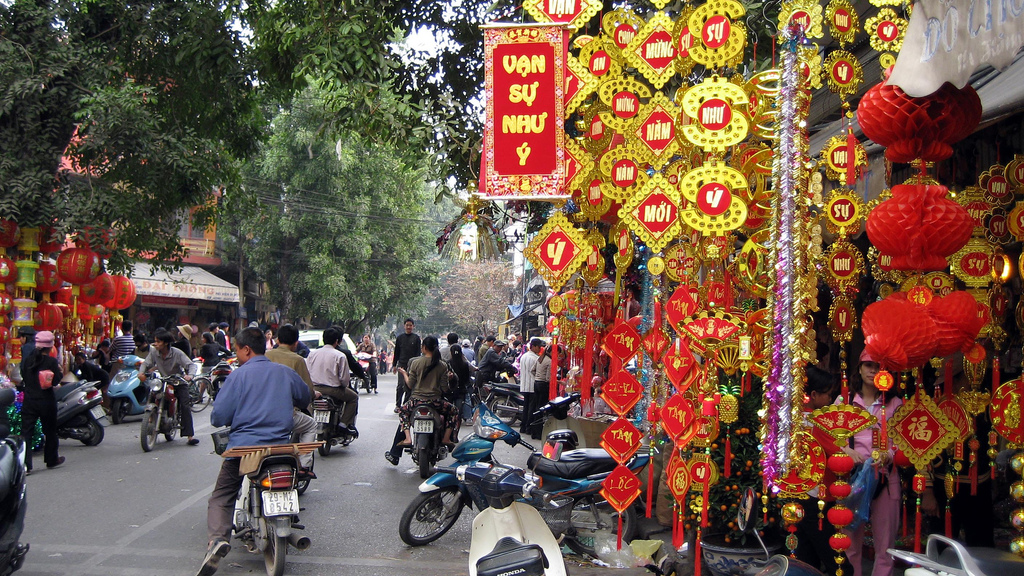

Despite officially being a three-day affair, festivities may continue for a week or more with every effort made to indulge in eating, drinking, and enjoyable social activities. It is also a time for family reunions, and for paying respect to ancestors and the elders. Gifts of food are made to friends, neighbors and relatives in the days before Tet.
Tet, above all, is an opportunity for the household genies to meet, those who have helped during the year, namely the Craft Creator, the Land Genie and the Kitchen God. Tet is also a chance to invite and welcome deceased ancestors back for a family reunion with their descendants to join the family's Tet celebrations. Finally, Tet is a great time for family members to meet up.

This custom has become sacred and secular, therefore, no matter where they are or whatever the circumstances, family members find ways to come back to meet their loved ones, gather for a dinner of traditional foods like bánh chưng (a square cake made of sticky rice stuffed with beans and pork), canh măng (a soup of boiled bamboo shoots and flied pork) and xôi gấc (orange sticky rice). This is followed by a visit to the local pagodas.

Everyone is in a rush to get a haircut, buy new clothes, spruce up their homes, visit friends, settle outstanding debts, and stock up on traditional Tet delicacies. Businesses hang festive red banners which read "Chuc Mung Nam Moi" (Happy New Year) and city streets are festooned. With colored lights. Stalls spring up all over town to sell mut (candied fruits and jams), traditional cakes, and fresh fruit and flowers.
Certain markets sell nothing but cone-shaped kumquat bushes. Others sell flowering peach trees, symbols of life and good fortune which people bring into their homes to celebrate the coming of spring. As vendors pour into the City with peach trees strapped to their bicycles, the streets look like moving pink forests.
The "Mam Ngu Qua"
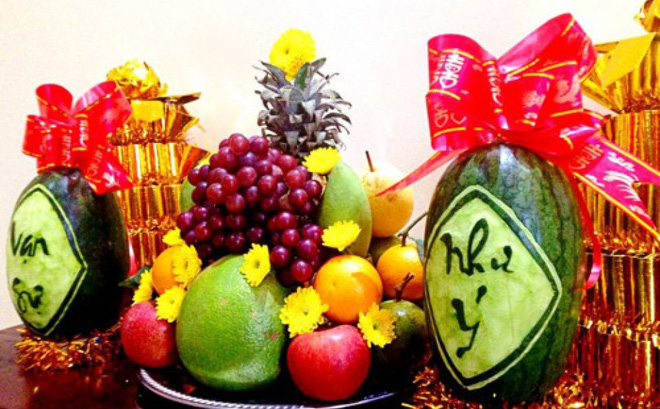
The "five-fruit tray" on the ancestral altar during the Tet Holidays symbolizes the admiration and gratitude of the Vietnamese to Heaven and Earth and their ancestors, and demonstrates their aspiration for a life of plenty. Legend said abot of theories but in a simpler way, the five fruits represent the quintessence that Heaven and Earth bless humans. This is one of the general perceptions of life of the Vietnamese, which is "When taking fruit, you should think of the grower".
Dao, Mai, Quat (the Peach, Apricot and Kumquat)
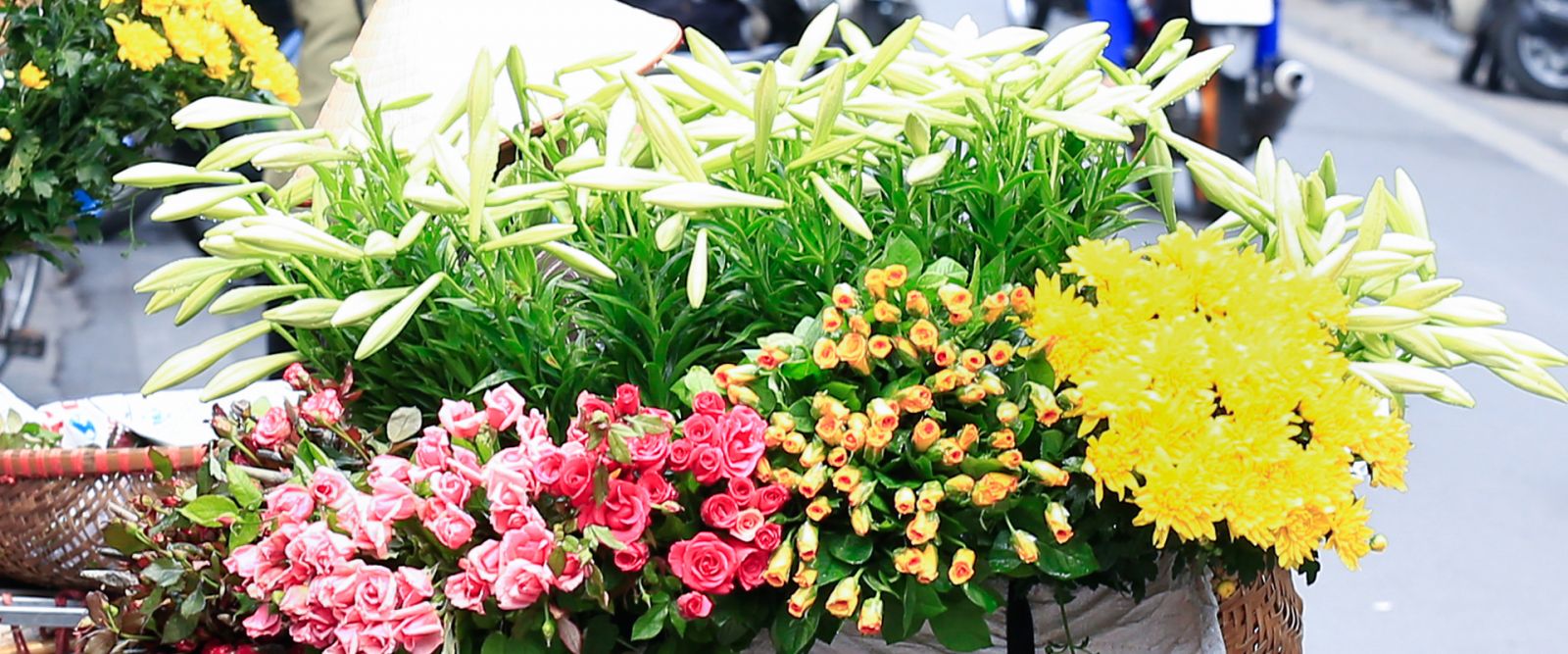
Coming to Vietnam during the season of the Tet festival, the visitor is engulfed in an ocean of colorful flowers. Visiting flower shows, contemplating the buds and blooms, and purchasing blossoms represents one of the distinct Vietnamese cultural characteristics. The peach blossoms (in the North) and the apricot blossoms (in the South) are symbols of the Vietnamese Tet.
The warm pink of the peach blossoms could very well match the dry cold of the North, but the hot South seems to be flourishing in the riot of the yellow of the apricot. The mandarin is symbolic of good fortune and, therefore, people tend to choose the little plants laden with fruit, big and orange, and verdant leaves for a longer display.
The giao thua (New Year's eve)
The Giao Thua is the most sacred moment, the passage from the old to the new year. It is popularly believed that in Heaven there are twelve Highnesses in charge of monitoring and controlling the affairs on earth, each of them taking charge of one year. The Giao Thua is the moment of seeing off the old chieftain upon the conclusion of his term and welcoming in the new one upon his assumption of office. For this reason, every home makes offerings in the open air to pray for a good new year.
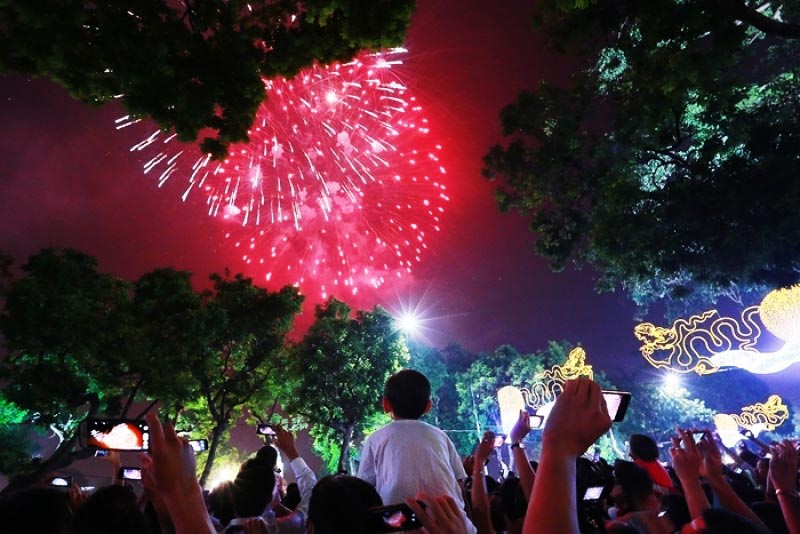

The very first moment after the Giao Thua is the start of the new year with many customs and practices, amusements and entertainment, all of a distinct Vietnamese folk culture. If you have an opportunity to visit Vietnam during the Tet Holidays and to welcome the Tet Festivities, together with the Vietnamese people, you will surely be profoundly impressed by the distinct traditional culture that is rich in national identity.
Food specialties for TET
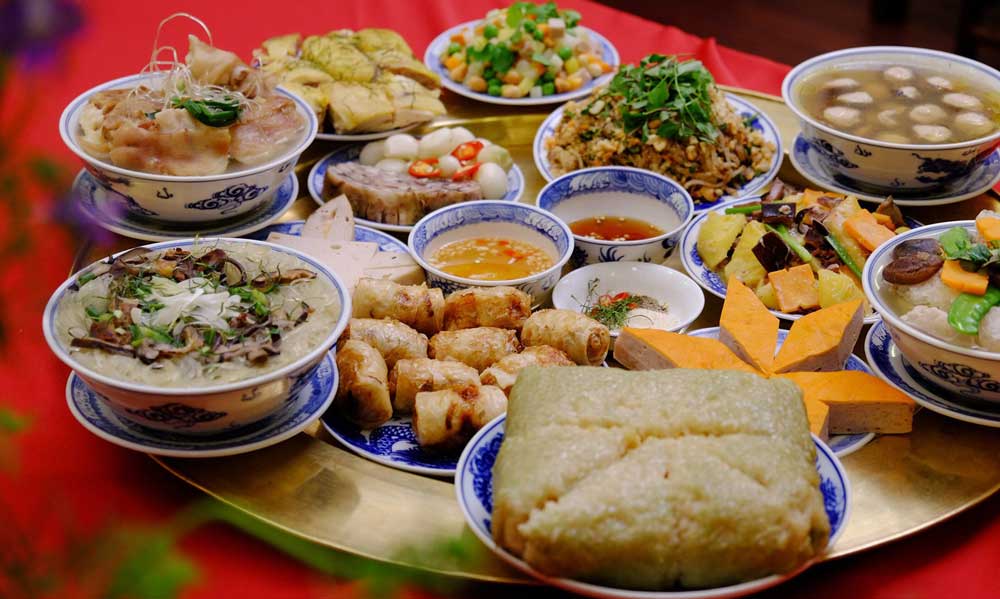

In the last day of the old year, the preparation of food to offer to the ancestors is of special significance. Dishes to offer to the ancestors differ in the Northern, Central and Southern parts of the country, depending on their respective weather conditions at the time and on different local agricultural products available.
What is common in all regions of the country during Tet holidays are the varieties of soups, fried, boiled, or stewed dishes, meat, fish, vegetable... The foods that the Vietnamese eat during Tet are varied and diverse What they have in common is that the people throughout the country all want to have the best and the most beautiful looking food on this occasion to offer their ancestors and to treat their friends and guests.
Starting Dates in Western Calendar 31 Jan 2014, 19 Feb 2015, 8 Feb 2016, 28 Jan 2017, 16 Feb 2018, 5 Feb 2019, 25 Jan 2020, 12 Feb 2021










